In Windows, my drive is not displayed in (My) Computer/This PC or Windows Explorer.
New internal Seagate brand drives are not partitioned or formatted from the factory. Only external drives are sold pre-formatted.
If your additional drive is new or completely erased, then to be visible in (My) Computer / This PC, it must be partitioned. In Windows you may use the Disk Management Utility to partition the drive.
Here is the order of actions, and we will expand on these below.
• Connect and install secondary drive.
• Boot into Windows.
• Open Computer Management and select Disk Management.
• Initialize, Partition and Format the drive.
Note: Even though you can see the drive in Disk Management it will not be visible in Windows Explorer until it has been initialized and partitioned.
Initializing and partitioning a drive:
1. On your keyboard press the Windows key ( ) + R
) + R
2. Type compmgmt.msc and press enter.
3. The Computer Management window will open.
4. Choose Disk Management under the Storage category.
Note: Windows will normally see the uninitialized drive when you open Disk Management and start the wizard to initialize the disk for you. In case the “Initialize Disk” wizard doesn’t start you may follow the instructions to manually initialize your disk:
5. Right-click on the Disk that needs to be initialized.
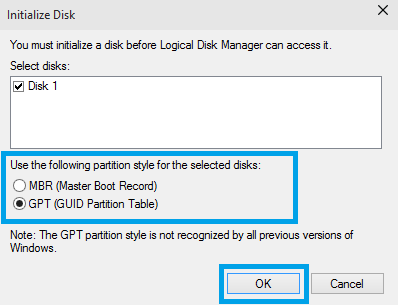
6. From the menu select Initialize Disk.
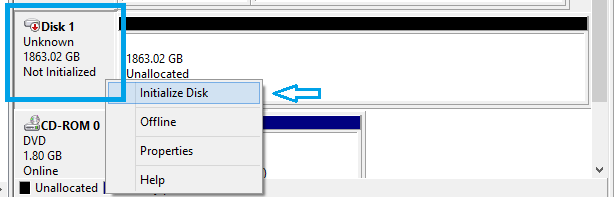
7. Select the appropriate partition style, MBR or GPT.
Note: The MBR Partitions can define a disk drive capacity up to 2.2TB. Windows operating systems that boot from an MBR are therefore limited to 2.2TB per MBR. The MBR Partitions can define a disk drive capacity up to 2.2TB. Windows operating systems that boot from an MBR are therefore limited to 2.2TB per MBR. GUID Partition Tables (GPT) can define drives larger than 2.2TB.
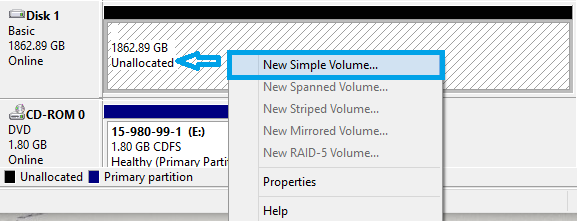
8. Once the disk is initialized, the partition will show Unallocated.
9. Right-click somewhere on the Unallocated partition.
10. From the menu select New Simple Volume.
11. The New Simple Volume Wizard will prompt.
12. Click Next.
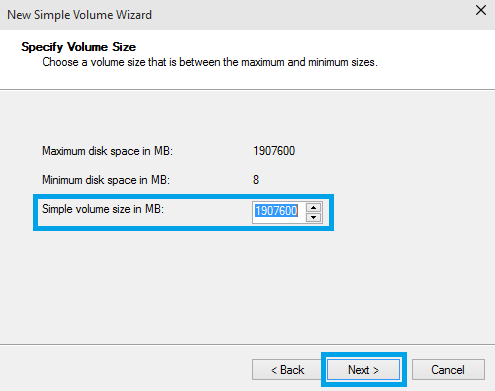
13. Specify Partition size in MB and click Next.
Note: If you want to create multiple partitions, change the Simple volume size in MB to the size of the partition you'd like to create.
14. Assign a Drive Letter then click Next.
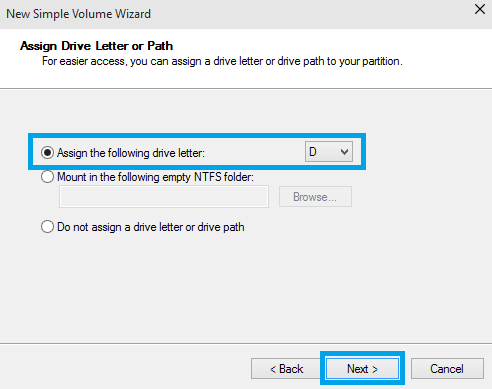
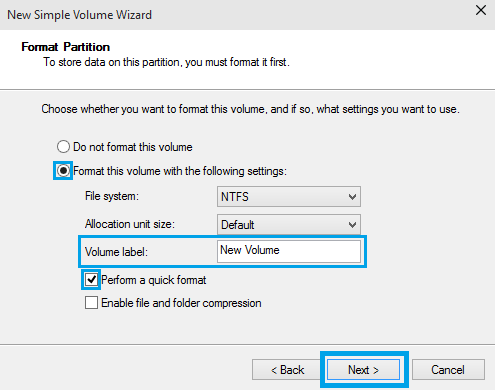
15. Specify the formatting options you want to use:
• File System
• Volume label
16. Click Next.
17. Confirm that the options selected are correct, and then click Finish.
18. Once you have clicked on the Finish button, the New Partition Wizard will close. In a few seconds, the "Unallocated" partition will say "Formatting". When the drive has completed formatting it will display as a healthy drive with the size and type of partition below the volume name and drive letter.
Additional information about Drives beyond 2.2 TB:
Most legacy systems built before 2011 have a traditional PC BIOS. This type of BIOS uses a Master Boot Record (MBR). The MBR Partitions can define a disk drive capacity up to 2.2TB. Windows operating systems that boot from an MBR are therefore limited to 2.2TB per MBR. A 3TB disk drive in a legacy BIOS and Window system will need a DiscWizard device driver to access the full capacity of a 3TB disk drive. Two partitions will be necessary because of the MBR limitation. The device driver mounts the capacity above 2.2TB with another MBR which looks to the system as a second virtual “physical” device.
GUID Partition Tables (GPT) can define drives larger than 2.2TB. You can use GPT today on any Windows 10 / 8 / 7 and Vista system as a non-booting data drive. Windows can only boot a GPT partition on a new type of BIOS called UEFI.
UEFI BIOS desktop systems are new since 2011. Windows 10/ 8 / 7 and Vista 64-bit operating systems support booting from UEFI and GPT without the need of a non-Microsoft device driver. This is the Windows native solution for booting a 3TB drive to a single partition.
 ) + R
) + R